IOS应用程序内部揭秘
1。Applications
Applications, therefore, are actually folders that contain the compiled binary, plus any resources they may need. The structure of applications differs slightly between OS X and iOS, but the fundamental philosophy of how an application is packaged remains the same. You can take a look inside an application by right-clicking one in the Finder and choosing Show Package Contents.
When you compile a project in Xcode and generate an application, Xcode creates the application package, and copies in any necessary resources. If you’re creating a Mac application, you can then just zip it up and send it to anyone for them to run it. On iOS, it’s a little different, because apps must be code-signed and provisioned before being run on the device.
One advantage to this is that applications are entirely self-contained and can be moved anywhere on a Mac.
2 Frameworks
Frameworks, which are loadable bundles of code and resources that other ap‐ plications (including your own) can use. Frameworks are actually very similar to ap‐ plications in structure—they contain a binary file and any resources—but they’re not standalone and are designed to be used by other apps.
3 一个Application里面包含了什么
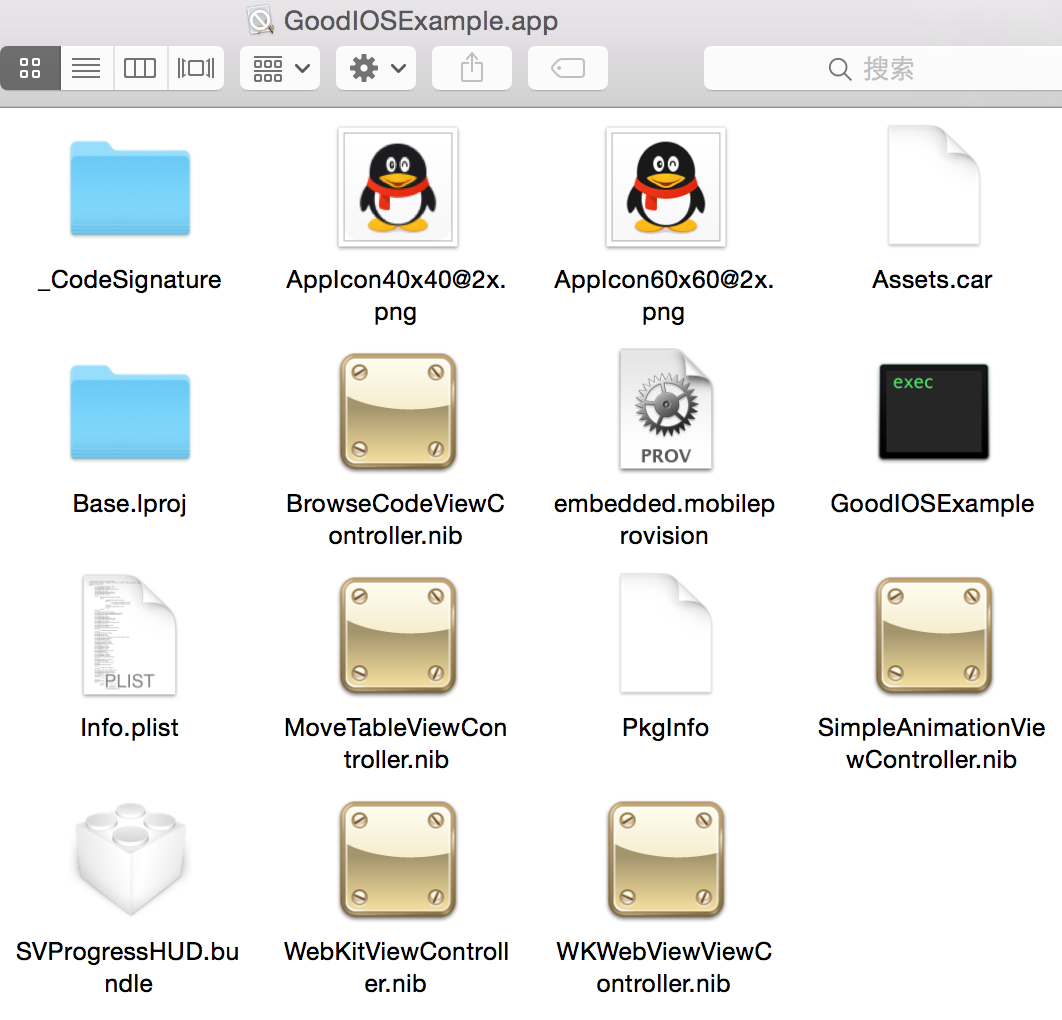 • 编译好的二进制文件
• 编译好的二进制文件
• 信息描述文件 Info.plist , 这个文件非常重要,如果我们删除了他,程序就不能启动。
• 资源文件.
4 Info.plist.
Information describing the app to the system is saved in a file called Info.plist. Among other things, Info.plist contains:
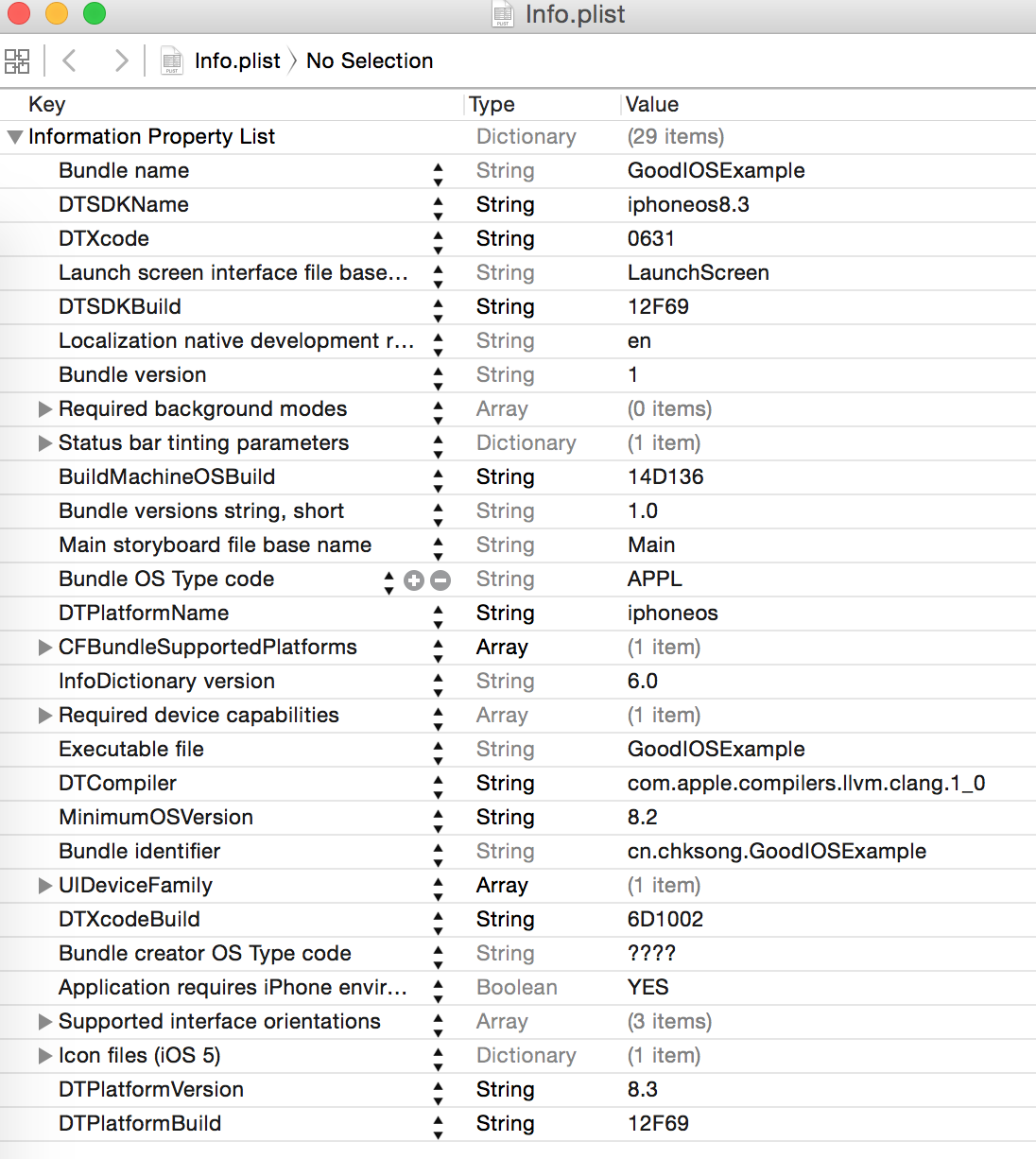
• App的 icon file
• What kinds of documents the application can open
• 编译好的的二进制文件名字
• The name of the interface file to load when the application starts up
• What languages the application supports (such as French, English, etc.)
• Whether the application supports multitasking (for iOS apps)
• The Mac App Store category the application is in (for OS X apps)
5 在Applicaton内部 通过NSBundle来找资源文件。
这对于ios程序非常有用途,因为程序在安装的时候,可能被安装任何的地方。
当我们的程序运行时,我们可以通过NSBundle,知道我的代码运行在磁盘的位置并且找到已经编译的资源。在NSbundle的帮助下我们不用关注我们运行的平台。
获得资源的路径
let resourcePath = NSBundle.mainBundle() .pathForResource("SomeFile", ofType: "txt")
获得资源的URLs
let resourceURL = NSBundle.mainBundle() .URLForResource("SomeFile", withExtension: "txt")
5 NSBundle 应用举例
NSBundle *bundle = [NSBundle bundleForClass:self.class];
NSURL *url = [bundle URLForResource:@"SVProgressHUD" withExtension:@"bundle"];
NSBundle *imageBundle = [NSBundle bundleWithURL:url];
UIImage* infoImage = [UIImage imageWithContentsOfFile:[imageBundle pathForResource:@"info" ofType:@"png"]];
imageBundle URLForResource:@"info" withExtension:@"png"] ;
file:///var/mobile/Containers/Bundle/Application/F8448D71-5CBB-4DF2-B58E-A84C588C92E1/GoodIOSExample.app/SVProgressHUD.bundle/info.png
[imageBundle pathForResource:@"info" ofType:@"png"]
@"/var/mobile/Containers/Bundle/Application/F8448D71-5CBB-4DF2-B58E-A84C588C92E1/GoodIOSExample.app/SVProgressHUD.bundle/info.png"